Rehabilitation Support Careers in Healthcare Settings
Rehabilitation support careers offer meaningful opportunities to make a tangible difference in patients' lives by helping individuals regain mobility, independence, and confidence after injury, illness, or surgery. These roles exist across diverse healthcare environments, from hospitals and outpatient clinics to nursing homes and home health agencies. Professionals in this field work closely with patients to implement personalized care strategies, guide mobility improvement exercises, and support long-term recovery goals. Whether you are exploring entry points into healthcare or considering a career transition, understanding the scope, responsibilities, and pathways within rehabilitation support can help you make informed decisions about your professional future.
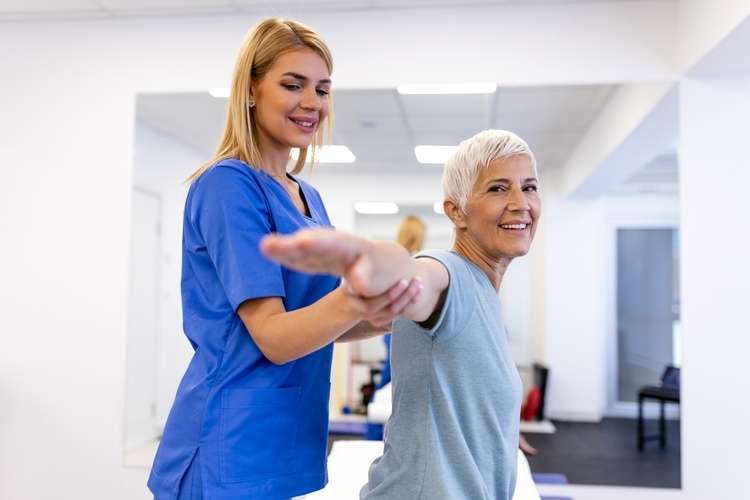

Rehabilitation support careers encompass a range of roles dedicated to helping patients recover physical function and improve quality of life. These positions are integral to healthcare teams, working alongside physicians, nurses, and therapists to deliver comprehensive care. Professionals in this field may assist with implementing treatment plans, monitoring patient progress, and providing hands-on support during therapy sessions. The work is both physically and emotionally rewarding, requiring patience, empathy, and strong communication skills. As healthcare systems worldwide continue to prioritize patient-centered care and functional recovery, demand for skilled rehabilitation support staff remains steady across various settings.
What Does Rehabilitation Support Involve?
Rehabilitation support involves assisting patients in regaining physical abilities lost due to injury, surgery, chronic conditions, or age-related decline. Support staff help implement therapeutic exercises, monitor patient responses, and document progress under the supervision of licensed therapists. Daily tasks may include preparing treatment areas, guiding patients through prescribed movements, educating families on home exercise programs, and ensuring safety during sessions. These professionals serve as vital links between clinical teams and patients, often spending significant time building trust and encouraging individuals through challenging recovery processes. The role requires both technical knowledge of body mechanics and interpersonal skills to motivate and reassure patients during vulnerable periods.
How Does Mobility Improvement Guidance Work?
Mobility improvement guidance focuses on helping patients restore movement, balance, and functional independence. Rehabilitation support staff assist with gait training, transfer techniques, and exercises designed to strengthen muscles and improve coordination. They may use assistive devices such as walkers, canes, or parallel bars to safely guide patients through progressive activities. Effective mobility guidance requires understanding each patient’s baseline abilities, limitations, and goals. Staff members observe movement patterns, provide corrective feedback, and adjust support levels as patients gain strength and confidence. This hands-on work demands physical stamina, attention to detail, and the ability to adapt techniques to individual needs and responses.
What Is Personalized Care Planning?
Personalized care planning tailors rehabilitation strategies to each patient’s unique circumstances, medical history, and recovery objectives. Support staff contribute to this process by collecting patient information, observing functional abilities, and communicating observations to supervising therapists. Care plans may address mobility challenges, pain management, fall prevention, and activities of daily living. Plans evolve as patients progress, requiring ongoing assessment and adjustment. Effective personalized care recognizes that recovery timelines and methods vary widely among individuals. Support professionals play key roles in ensuring plans remain realistic, patient-centered, and aligned with broader treatment goals established by interdisciplinary healthcare teams.
Where Do Rehabilitation Support Professionals Work?
Rehabilitation support careers exist across numerous healthcare environments. Hospitals employ support staff in acute care units, rehabilitation departments, and specialized stroke or orthopedic centers. Outpatient clinics offer opportunities to work with patients recovering from surgeries or managing chronic conditions. Skilled nursing facilities and long-term care centers require rehabilitation support for elderly residents regaining function after illness or injury. Home health agencies send staff into patients’ homes to provide therapy assistance in familiar environments. Sports medicine facilities, pediatric centers, and veterans’ hospitals also employ rehabilitation support professionals. Each setting presents unique challenges and patient populations, allowing individuals to find environments that match their interests and strengths.
What Skills and Qualities Are Important?
Successful rehabilitation support professionals possess a combination of technical knowledge and interpersonal abilities. Physical stamina is essential, as the work often involves standing for extended periods, assisting with patient transfers, and demonstrating exercises. Strong communication skills help explain procedures, encourage patients, and collaborate with healthcare teams. Attention to detail ensures accurate documentation and safe execution of treatment protocols. Empathy and patience support patients through frustrating or painful recovery phases. Problem-solving abilities enable staff to adapt approaches when patients struggle or encounter setbacks. Reliability and professionalism maintain trust within clinical teams and with patients who depend on consistent, quality support throughout their rehabilitation journeys.
What Are Typical Career Pathways?
Entry into rehabilitation support careers varies by region and specific role. Some positions require completion of certified programs or associate degrees in rehabilitation therapy, physical therapy assisting, or related fields. Others offer on-the-job training for candidates with healthcare backgrounds or relevant experience. Many professionals begin in entry-level support roles and advance through additional education, certifications, or specialization in areas such as geriatrics, pediatrics, or sports rehabilitation. Career progression may lead to supervisory positions, specialized clinical roles, or transitions into licensed therapy professions through further education. Continuing education opportunities help professionals stay current with evidence-based practices and emerging rehabilitation techniques.
Rehabilitation support careers offer fulfilling opportunities to directly impact patient recovery and quality of life. These roles require dedication, compassion, and commitment to helping individuals overcome physical challenges and regain independence. As healthcare continues evolving to emphasize functional outcomes and patient engagement, skilled rehabilitation support professionals remain essential members of care teams across diverse settings worldwide.