Essential Equipment for Effective Diabetes Control
Managing diabetes effectively requires the right tools and supplies to monitor blood glucose levels, administer medications, and maintain overall health. From blood glucose meters to insulin delivery systems, having access to proper diabetic supplies is crucial for daily management and long-term health outcomes. Understanding what equipment you need and how to use it properly can make a significant difference in maintaining stable blood sugar levels and preventing complications.
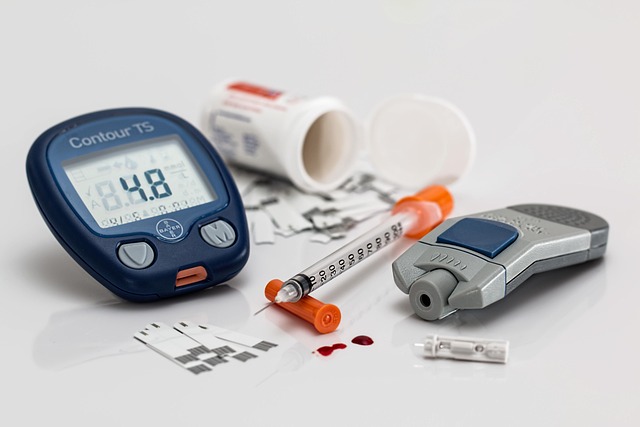
Understanding Basic Diabetic Supply Categories
Diabetic supplies include tools for monitoring and daily management that are essential for anyone living with diabetes. These supplies fall into several key categories: blood glucose monitoring equipment, insulin delivery systems, testing materials, and emergency supplies. Each category serves a specific purpose in helping individuals track their condition and respond appropriately to changes in blood sugar levels.
Blood glucose meters are the cornerstone of diabetes management, allowing for regular monitoring throughout the day. Modern meters are compact, accurate, and often connect to smartphone apps for easy tracking. Test strips, lancets, and alcohol swabs complete the basic monitoring kit that most people with diabetes use multiple times daily.
Information About Diabetic Supplies and Their Functions
Information about diabetic supplies helps individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare needs. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) represent advanced technology that provides real-time glucose readings without frequent finger pricks. These devices use small sensors placed under the skin to track glucose levels continuously and can alert users to dangerous highs or lows.
Insulin delivery methods vary from traditional syringes and vials to modern insulin pens and pump systems. Insulin pens offer convenience and precise dosing, while insulin pumps provide continuous delivery for those requiring intensive management. Each method has specific advantages depending on lifestyle, treatment requirements, and personal preferences.
Healthcare Provider Guidance for Supply Selection
A healthcare provider can guide you on what supplies you may need based on your specific type of diabetes, treatment plan, and lifestyle factors. Type 1 diabetes typically requires more comprehensive supplies including insulin delivery systems, while Type 2 diabetes management may focus more on monitoring equipment and oral medications.
Your healthcare team will consider factors such as frequency of testing required, insulin needs, dexterity issues, vision concerns, and insurance coverage when recommending specific supplies. Regular consultations help ensure your supply kit remains appropriate as your condition and treatment needs evolve over time.
Essential Monitoring Equipment and Accessories
Core monitoring supplies include blood glucose meters, test strips, lancets, and control solutions for meter accuracy checks. Many people also benefit from having a glucose logbook or smartphone app for tracking patterns and sharing data with healthcare providers. Ketone testing strips are important for those with Type 1 diabetes or during illness.
Additional accessories like carrying cases, extra batteries, and backup meters ensure you’re prepared for daily activities and travel. Sharps containers provide safe disposal for used lancets and syringes, while alcohol swabs maintain hygiene during testing procedures.
Emergency Supplies and Preparedness
Emergency preparedness requires having backup supplies and quick-acting treatments readily available. Glucose tablets, glucose gels, or other fast-acting carbohydrates help treat low blood sugar episodes. Glucagon emergency kits are essential for severe hypoglycemic episodes, particularly for insulin users.
Maintaining adequate supply reserves prevents interruptions in care during emergencies, travel, or supply chain disruptions. Most healthcare providers recommend keeping at least a 30-day backup supply of essential items like test strips, insulin, and medications.
| Supply Category | Examples | Estimated Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Glucose Monitoring | Meter, test strips, lancets | $50-150 |
| Insulin Delivery | Pens, syringes, pump supplies | $100-400 |
| Continuous Glucose Monitor | Sensors, transmitter | $200-350 |
| Emergency Supplies | Glucose tablets, glucagon kit | $20-50 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Storage and Maintenance Considerations
Proper storage of diabetic supplies ensures accuracy and safety. Insulin requires refrigeration but should not freeze, while test strips need protection from moisture and extreme temperatures. Most supplies have expiration dates that must be monitored to maintain effectiveness.
Regular maintenance includes cleaning meters according to manufacturer instructions, rotating injection sites to prevent tissue damage, and replacing worn equipment as needed. Keeping supplies organized and easily accessible supports consistent daily management routines.
Effective diabetes management relies heavily on having the right supplies and using them consistently. Working closely with healthcare providers, staying informed about new technologies, and maintaining adequate supply reserves creates a foundation for successful long-term diabetes care. Regular evaluation of your supply needs ensures your management plan remains effective as technology advances and your health needs change.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.